Chapter 2 of Getting Started with Google Ads: Campaigns and Structured Delivery
Members only · Non-members can read 30% of the article.
- Published
- September 16, 2025
- Reading Time
- 4 min read
- Author
- Felix
- Access
- Members only
Non-members can read 30% of the article.
Before you begin, list the proper nouns that appear in the article:
ROAS (Return On Ad Spend, return on ad spend): Formula = Revenue ÷ Ad Spend. Example: Spending 1,000 yuan brings in 3,000 yuan in income → ROAS = 3.
tROAS (Target ROAS, target return on advertising spend): Smart bidding strategies. Set a target return rate (such as 300%), and the system will use machine learning to automatically adjust prices to try to make the overall advertising reach this level.
tCPA (Target CPA, target customer acquisition cost): Smart bidding strategies. Set a target conversion cost (such as 50 yuan/lead), and the system will automatically bid to control the average cost close to the target.
Campaign: The top-level container for advertising, which determines budget, bidding strategy, delivery area, series type, etc.
Ad Group: The "topic warehouse" under the series determines the combination of keywords/audiences and advertising materials to ensure relevance.
PMax (Performance Max, effect maximization series): Google's fully automated advertising campaigns are uniformly placed on Search, YouTube, GDN, Discover, Gmail, Maps and other placements. High-quality materials and data support are needed.
RSA (Responsive Search Ads, adaptive search ads): The default ad format on Google Search. You provide multiple titles and descriptions, and the system automatically combines and tests the optimal version.
SKAN(SKAdNetwork): Apple iOS's privacy attribution framework is used for app delivery effect reporting. Data granularity is limited and mapping needs to be configured in advance.
UTM (Urchin Tracking Module, tracking parameters):
Tag parameters added after the URL (such as ?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc) are used to distinguish traffic sources and advertising effects.
gclid/wbraid/gbraid: Click ID automatically generated by Google Ads, used to track conversions and correspond to ad clicks.
CPC (Cost Per Click, click cost): Ad spend ÷ clicks. The actual amount you pay for each click on your ad.
CTR (Click Through Rate, click rate): Clicks ÷ Impressions. A direct indicator of ad appeal and relevance.
CVR (Conversion Rate, conversion rate): Conversions ÷ Clicks. Measure how well your landing page matches your advertising promise.
CPA (Cost Per Acquisition, customer acquisition cost): Average ad spend to get one conversion (purchase/signup/lead).
LTV (Lifetime Value, customer lifetime value): The total revenue a customer is expected to bring in over its lifetime.
tCPI (Target Cost Per Install, target cost per installation): You want to capture the average cost of an app install through advertising.
Lead: Potential customer information, such as form submission, telephone consultation, and appointment. Lead quality determines subsequent conversion results.
CPM (Cost Per Mille, cost per thousand impressions): CPM is more suitable for brand exposure (even if you see it),
CPV (Cost Per View, cost per view)
Auction insights: The bidding data provided by Google allows you to see the overlap rate, surpassing rate, and top display rate between you and your competitors.
Value Tracking/Value Passing: In Google Ads, "conversion" is not just an event (such as someone placing an order), but can also have a value field.
Learning Phase: This refers to the stage when the Google system needs to re-collect data and explore the optimal delivery method after a campaign or ad group is newly created or has undergone major changes.
Pacing (pace/money burning speed): Budget and bid control of intraday/weekly consumption.
Shared Budget: Multiple series share a single budget.
Bid Strategy: Max Conversions / Max Conversion Value / tCPA / tROAS.
1. Campaign
The definition of Campaign is a container for the same delivery target and rules.
- You decide at the series level:
- Series type (Search/Display/YouTube/Shopping/Performance Max/App).
- Target and bid strategies (Max Clicks/Max Conversions/tCPA/tROAS).
- Budget (daily budget or shared budget).
- Region, language, delivery period, network and frequency control (display/video).
- Conversion goal: Select Conversion actions for bidding.
This layer controls "money and direction". Budgets and learning periods take effect at this level; brand and non-brand, different languages/markets, and cold/hot traffic should be split into different campaigns.
In addition, if the goals are different (tCPA vs tROAS), the budget needs to be controlled separately, the region/language needs to be independent, and the series types are different, a new Campaign needs to be created.
Next, let’s create a
Campaignfirst.
Step one: Select promotion objectives (Objectives)
The first step in creating a series is usually to choose an objective.
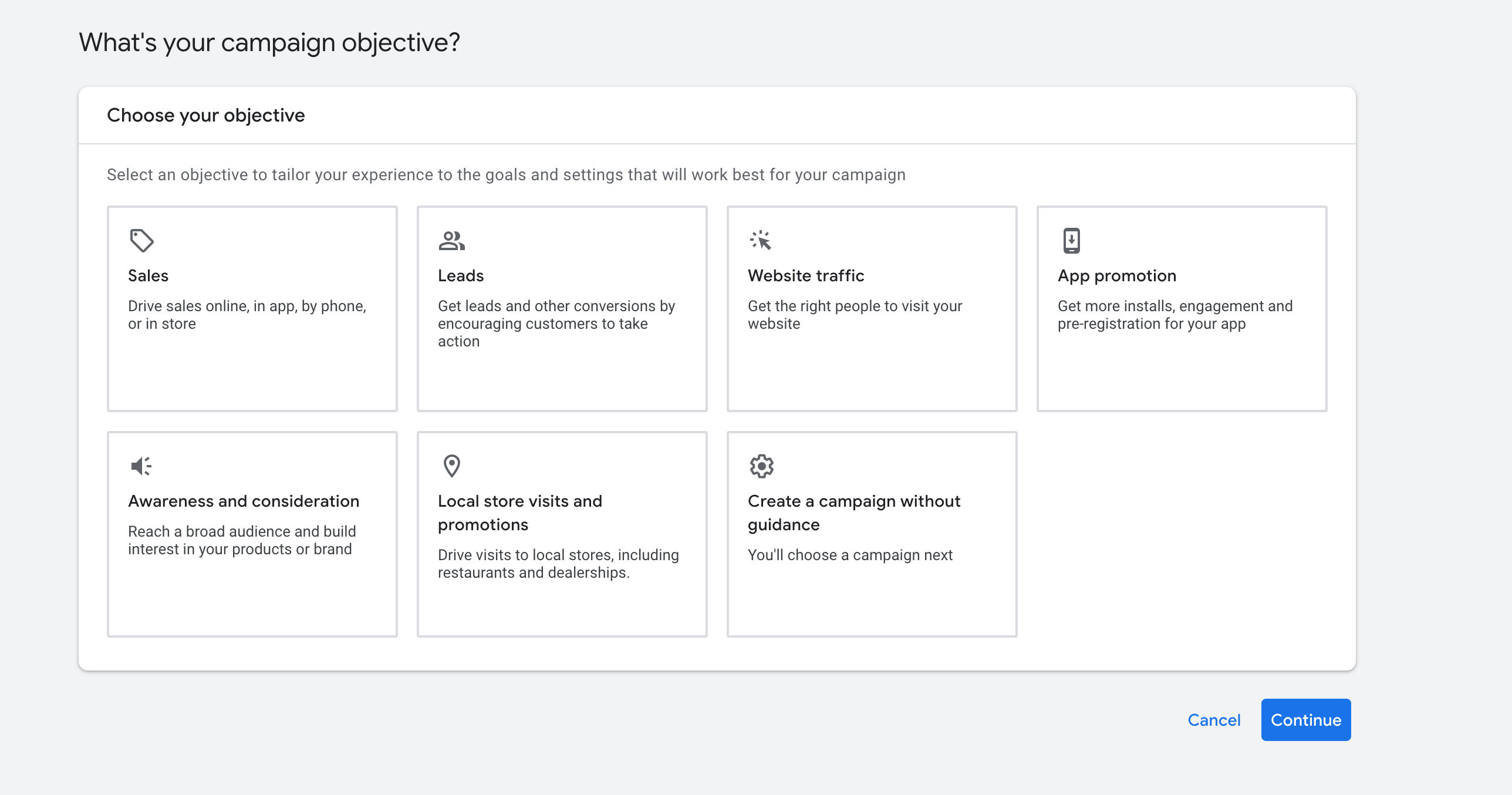
- Sales: Target orders/revenue, and default to Maximize conversion value/tROAS. Suitable for e-commerce or businesses with transferable amounts (value transfer is required. If you only transfer the number of conversions, the system will optimize the "quantity". If the value is transferred, the system can optimize the "value" and help you invest your budget in higher value groups).
- Leads (potential customers): Target leads, default Maximize conversions/tCPA. Good for B2B/service industries; use high-quality “main conversions” (e.g. qualified leads/phone calls) and avoid setting low-quality micro-conversions as the main goal.
- Website traffic: Target clicks, default Maximize Clicks/Manual CPC. It is suitable for short-term temperature measurement in the early stages of cold start or when the material/tracking is not ready. It is not suitable for long-term use to avoid deviation from business goals.
- App promotion: Dedicated to AC series (App Campaigns), targeting events such as installation/first opening/registration/payment, etc. tCPI/tCPA or value bidding is commonly used.
- Awareness and consideration: Targeting reach/viewing, common billing is CPM/CPV, video/display delivery suitable for brand appeal, weak conversion orientation, needs to be connected with remarketing.
- Local store visits and promotions: Cooperate with location expansion and local inventory to optimize visits to stores or phone calls, suitable for offline store-type businesses.
- Create a campaign without guidance: No preset goals, all settings
Subscribe to unlock the full article
Support the writing, unlock every paragraph, and receive future updates instantly.
Comments
Join the conversation
No comments yet. Be the first to add one.